We have a lot of options to create permanent marks on material surfaces. One of them is laser-etching. So question arises: what is laser etching? You can say it is the branch of the laser marking process but is different in methods and results.
We will cover in this blog in detail: what is Laser-machine Etching-process? Its types and why it is more reliable than other techniques like chemical-etching, dry-etching, laser marking, etc.
To explore this technology, Let’s go in-depth to analyze it.

What is laser Etching?
It is a process of creating permanent marks on materials surfaces by melting surfaces with high-power laser beams. By this, a small amount of surface-material removes. You can say it is a subtracted method of marking.
It is used in many industries to label their parts and machines for identification purposes. Mostly numbers and barcodes are marked by this technique.
This application gives an excellent contrast between the materials and the label code, and this is especially useful when scanning materials codes.
Etching-Material Depth
This process depth is up to 0.0001 inches or 2.54 micrometers, and it will consider laser-engraving if the lazer etching-depth exceeds this limit.
Before going to the next step, takes 10 minutes to read about lasers and their types. If you are familiar with the basics of laser, then go ahead!
Etching Material Process
It depends on the type of laser used in the machine. All these lasers are pulsed wave lasers.
When the high-power laser beam hits the specific part of the material-surface as our design is. It gains heat energy and expands: as a result, it melts the surface and leaves a permanent mark on it.
Laser Etcher Machine
The same laser machines can perform etching-design or engraving-design. The differences between these two are only in laser power.
As engravings creates deep marks, so etching-process needs less power to perform.
CO2 Laser-Etcher Machines
The CO2 lasers are used in these machines-types to etch designs on material-surfaces.
Diode Laser-Etcher Machines
The diode lasers are used in these machines to etched designs on material-surfaces.
Fiber Laser-Etcher Machines
The fiber lasers are used in these machines to etched designs on material-surfaces.
How to do Laser Etching Material? (5 Steps)
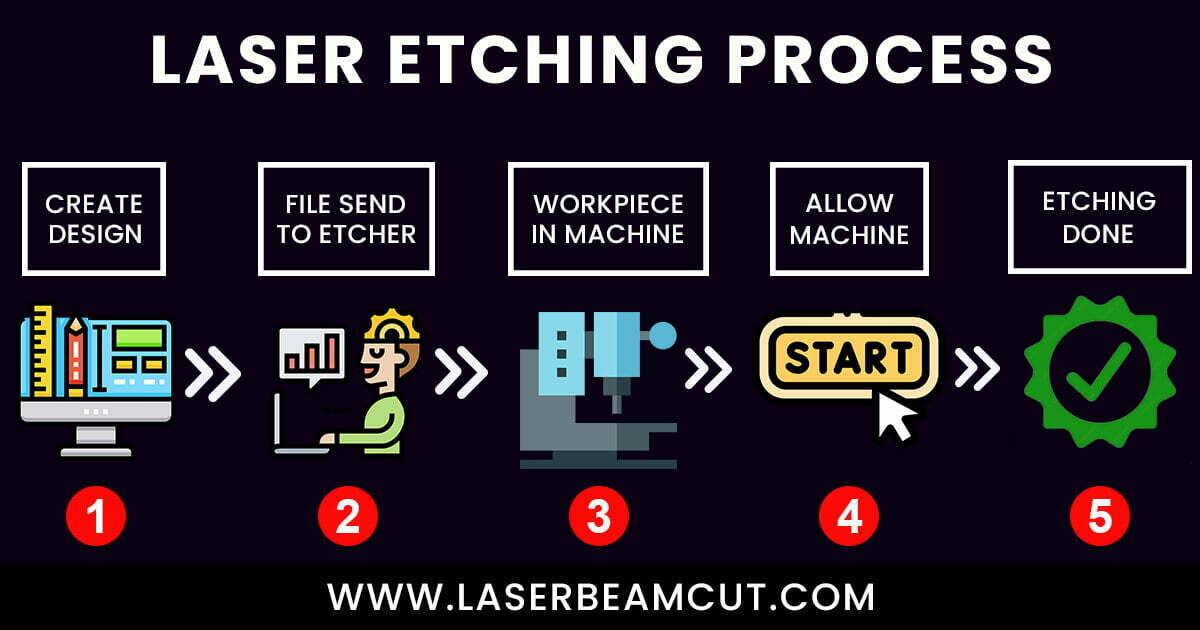
It contains five steps to etch designs on materials.
- Make Design
The first step is to draw a design on Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software that needs to etch on the material-surface.
Software’s are
- Adobe Illustrator
- Inkscape
- LightBurn
- Catia
- Pro e
- Solid work
- Select the laser for Etcher Machines – Choose the laser type that is best suited for your material.
Laser Type (Etcher Machines)
Applications CO2 Laser
Non-metal materials
Diode Laser
Both metal and non-metal materials
Fiber Laser Metallic-materials
- Send File to Laser etcher Machine
- Allow the machine to start
- The final lazer-etching design is applied to the surface of the material.
Laser Etching Parameters

It depends on the material-type and machine parameters.
Machine Parameters
Power
To etched-material, it should be greater than 30-watt power laser machines.
Machine Speed
The etcher you use should have a moderate speed setting. If the speed is too high, lazer-etching may not work on detailed drawing designs.
In comparison to laser-engraving, lazer-etching needs less speed as it needs less material-removal.
Laser Beam Spot Size
The spot size of the laser beam should be small to get high-quality etch results.
Material Type
As we know: Lazer-etching is a process to leave a permanent mark by melting material-surface. So it depends on the material type and its thickness.
Here are some melting points of some materials.
Melting Point of Materials | |
Materials | Melting Points |
Aluminum | 565-585°C |
Carbon Steel | 1425—1540°C |
| Lead | 327.5°C |
| Magnesium | 650°C |
| Stainless Steel Grade 304-316 | 1375—1450°C |
Laser Etch Coloring
Etch process left mark color is black, white, or grey. It depends on the material-surface.
- When you have a clean and reflected material-surface, it reflects the laser beams and leaves white marks.
- When you have a rough and absorbent material-surface, it absorbs the laser beams and leaves black or grey marks.
Materials for Laser Etching
Laser etcher machines can etch any material that can be laser engraved or cut. Some materials are listed below
- Metal
- Wood
- Steels
- Aluminum
Etching Laser Applications
Laser-Etching is commonly used in manufacturing industries to etch barcodes, serial numbers, and symbols in production lines to identify scanners. It makes speeds up production.
Etching-operations use in many industries, including automobiles, space technology, and medical tools manufacturing.
Product designers and artists often etch designs to make their designs look more appealing.
Other Etching-Methods
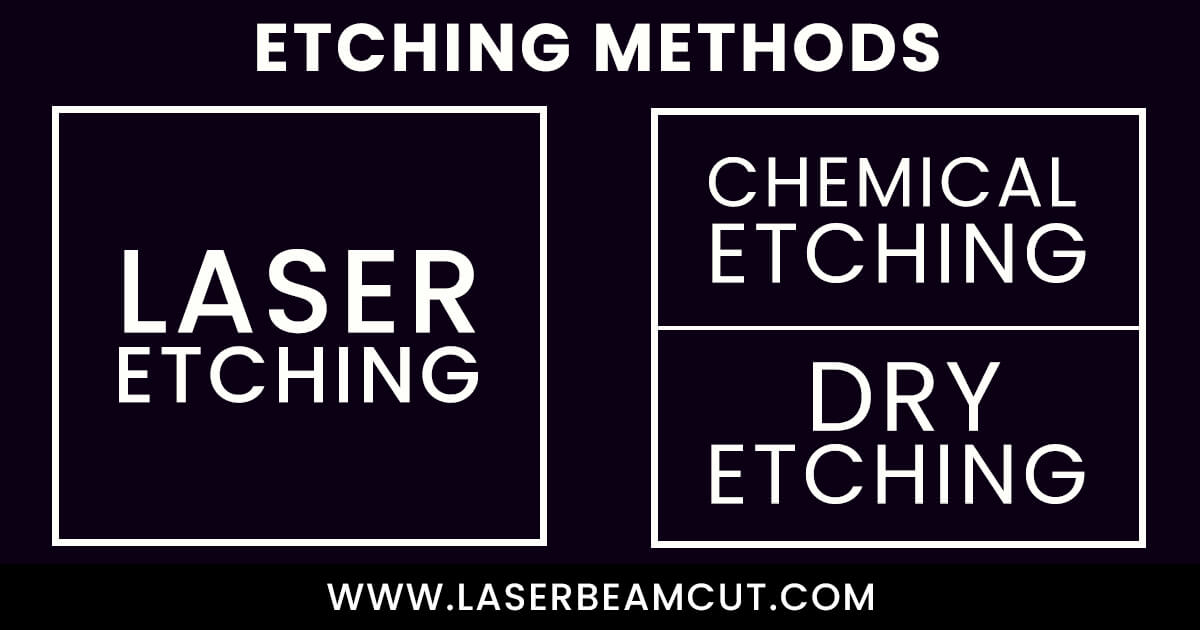
As laser-etch process, other methods are also available. Every etching-method has its benefits and limitations. We can choose one of them for our needs.
The most common etching-methods are
- Chemical Etching-method
- Dry etching-method
Chemical Etching-Method
As laser beams etch-materials in lazer etchings, the corrosive agent ( called etchant ) is used to etch by subjecting it; to where each part needs to be in the chemical etchings process. It is also called wet-etchings.
This method is used for mass production, as it can etch multiple products in a single operation. However, unless lazer etching-process has limitations in this aspect, it is best for where limited production.
Dry etching-Method
Dry etchings are a process in which material is removed by physical methods; or by reactive ion reactions. Plasma etchings are a type of dry etchings.
Etching-Material Advantages
It has various benefits, which are listed below.
- Economical and Reliable Machines
Laser etcher machines are less expensive and are portable machines.
- High-Quality Control
The machine can control its laser beam, and it gives high-quality results.
- Complex Design
It can etch complex designs.
- Lead Time
The process of etchings a single product can take a few minutes.
Limitations of Laser Etchings
It has limitations too, which are listed below.
- Mass production
This process is best for small-scale production, but it takes a long time if you go for mass production. It is due to its limitations on its ability to work on only one project at a time.
- Material strength
Laser beams melt the material, and this affects the strength of the material.
- Materials Thickness
When etchings thin-materials, you should avoid doing so with this process.
Laser Marking vs Etching-Design:
Laser marking and etchings both label parts or products. However, they each have different methods and different outcomes.
- Laser Marking is a process of making labels by discoloring material-surfaces without material removal.
- Lazer Etchings are a process to create a mark by melting material-surface and is thus called the subtractive method.
To make these terms more clear, I suggest you take five minutes to read this blog.
( the similarities and differences between laser engraving, marking, etch, embossing, and cutting )
Conclusion:
Lazer etching-material is a method of etch-materials by melting the surfaces of the material. It is best for low production but not recommended for mass production. To learn lazer etchings in detail, this would be helpful for you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. How many types of etchings are available in the market?
Ans: Three types
- Lazer Etchings
- Wet Etchings
- Dry Etchings
2. What type of lasers are used to etch materials?
Ans: Pulsed Wave Lasers
3. What is difference between Laser Marking and Etching-material?
Ans: Lazer Marking creates marks on the surface without any removal of surface-material while lazer etchings method removes surface-material to etch design on surface.
4. On which parameters, laser etching depends?
Ans: It depends on two parameters.
- Material-Properties ( Melting Point )
- Machine Parameters ( Speed, Power, Beam Spot Size)
5. What is maximum depth for laser etching?
Ans: Its maximum depth is up to 0.0001 inches or 2.54 micrometers, and it will consider lazer engraving if the lazer etchings depth exceeds this limit.

