We deal with many operations, such as cutting, welding, and polishing for metals to create the desired product. The most crucial part of the manufacturing process is cutting metals. We can use a laser for cutting metal.
Each metal has specific properties. These are dense and reflective materials. Due to this reason, metal cutting is not easy.
In this article, I will provide depth knowledge about laser cutting metal. It will also include a discussion on its future. So, are you ready? If yes, move on.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a cutting process that uses a laser beam to cut through metal. It is a precise and efficient method for manufacturing industries. A key benefit of laser cutting for metal is its ability to create complex shapes and designs quickly and accurately.
Recommended to read this article: “ Laser Cutting and Its Types”
How Does Laser for Metal Cutting Work?
When metals are under the laser beam, it vaporizes the metal surface to produce a cut as per instructions. It is the simple answer about how it works.
Now have a look at its working stages.
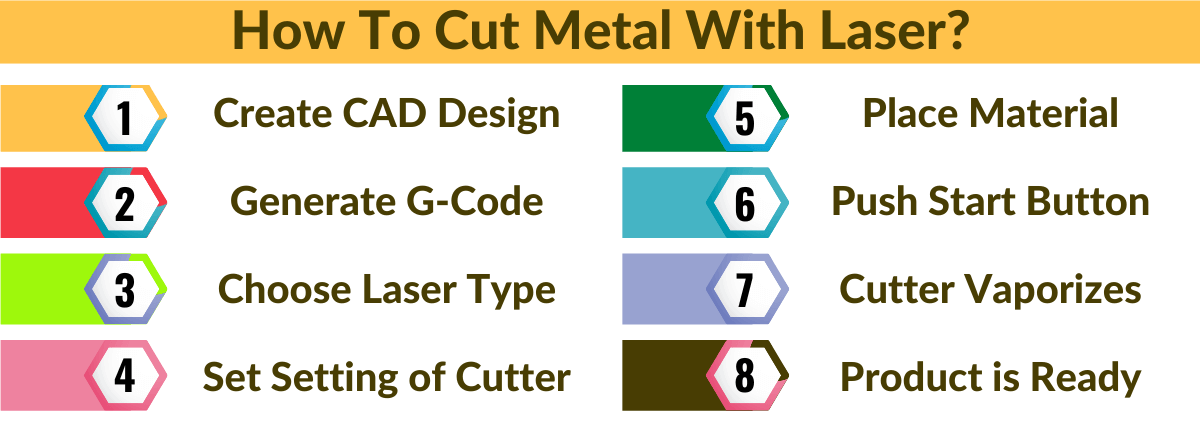
The Laser Cutting Process
It takes 5 Steps to cut metal material.
- Design on CAD software and generates its G-Code
- Choose the appropriate laser type
- Set cutter settings according to the metal type
- Place metal inside the machine and allow it to start
- The cutter vaporizes the metal surface to produce cut
Components of a Laser Cutter Machine
A laser-cutting machine consists of several key components, including
- Laser source – Produces High Power Beams
- Cutting head – Direct these beams on the metal surface
- Cutting bed – Hold Metal
- Computer-controlled system – Works as per G-Code instructions
Factors that Laser for Metal Cutting Depends
The speed and efficiency of the metal-cutting process depend on several factors:
- Metal Type
- Thickness of Metal
- Laser Type
- Shape or Design of cut
- Cutting speed, Frequency, and Wavelength of laser
Types of Lasers to Cut Metals
Metals are dense materials. And some have reflective properties. We should choose appropriate laser types to produce the precise metal cut.
Five laser types use in cutter machines. Metal-cutting operations for industry usually use CO2, Diode, and Fiber lasers.
CO2 Laser Cutters
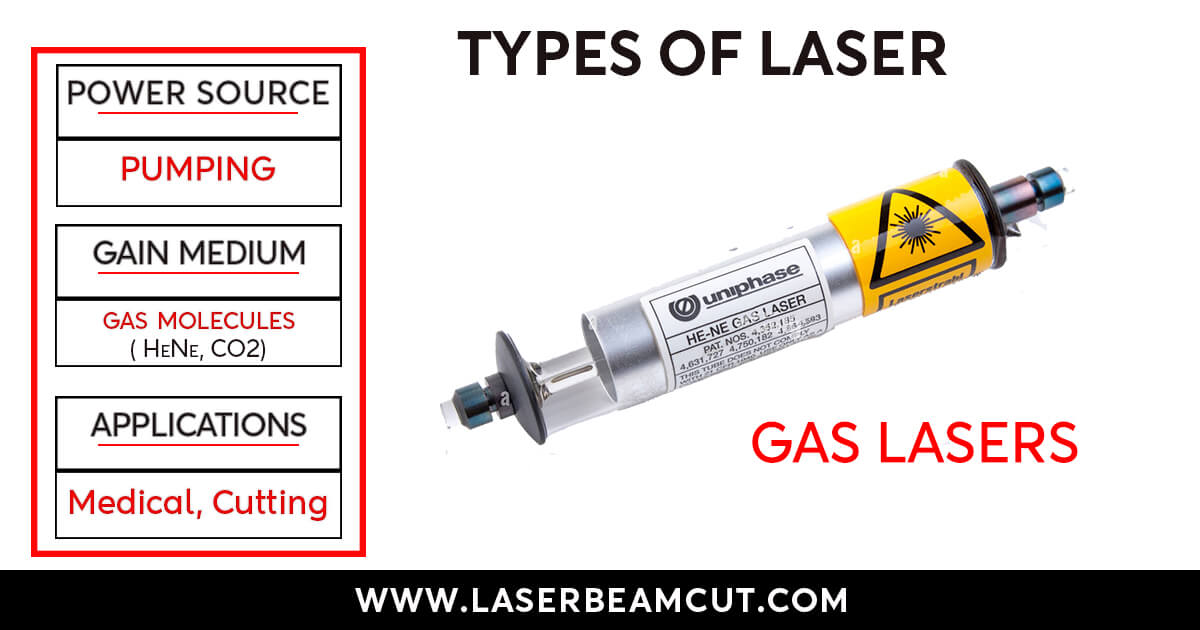
These laser cutters use a gas medium of CO2 as a power source. CO2 Cutters produce above 10,000 nm wavelengths.
CO2 cutters are best for thin metal sheets but unsuitable for rigid and reflective metals.
Sometimes, we can use this cutter to cut metals using high-power CO2 Lasers.
Diode Laser

The wavelength of these cutters is around 500 nm. That is comparatively low compared to CO2 lasers.
Diode lasers can cut aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. But it does not cut thick and hard metals.
Fiber Laser

These cutters are best for reflective metal surface materials. Their wavelength is around 1000 nm.
They are more energy-efficient and faster than CO2 and Diode lasers. Due to this, these are the popular choice for high-volume cutting applications.
What are the benefits of Laser Cutting for metal Materials?
We can cut metals with different techniques. But laser cutting gives various benefits. Such as
- Non-contact Cutting Method
- Precise and Safe
- Complex cutting possible
- Can cut reflective metals
- Low power consumption
- Less material loss
- High-speed operations
Applications of Laser Cutting Metals
We can use lasers for cutting metals for different applications.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry uses laser cutting for a wide range of applications. It includes cutting car bodies, engine parts, and other metal components. The high precision and accuracy offered by laser cutting make it an ideal choice for this industry.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry also uses laser cutting for various applications, including cutting aircraft components and parts. The precision and speed of laser cutting make it an essential tool for this industry.
Medical Industry
The medical industry uses laser cutting for medical devices and implant production.
Construction Industry
The construction industry uses laser cutting to produce metal components for buildings and structures.
Consumer Goods Industry
The consumer goods industry uses laser cutting for a wide range of applications. It includes cutting metal components for appliances, electronics, and other consumer goods.
Future of Laser Cutting Metal
Artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things are driving the 4th industrial revolution.
As machine learning and deep neural networks grow, these may also change the ecosystem of manufacturing industries.
Laser cutters would work fast and be efficient in decisions according to the requirements at the time of operation.
Internet of Things will be able to connect these cutters to cloud-based controllers. These controllers would control machines remotely from any place in the world.
In short, the future is bright for this technology. But we should be aware of current emerging technologies to make ourselves ready to use these technologies for our businesses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, laser cutting for metal is a precise and efficient method that offers several advantages over traditional methods. It is the popular choice for various industries to cut metals as it gives accurate kerfs.
There are various cutter types to cut metal based on a laser in the machine. Usually use CO2, Diode, and Fiber lasers for metal cuttings.
As technology continues to evolve, laser cutter machines will work smartly and efficiently in the future.
FAQs ( Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Will AI replace laser cutter machines?
No, AI will not replace cutter machines. It would enable cutters to make the right decisions in real-time operations. It increases the productivity of work.
2. How Does An Internet of Things Change the ecosystem of manufacturing industries?
This technology connects AI-based machines to cloud-based controllers. With this development, manufacturers can control the cutters on their cell phones.
3. Why can CO2 Cutters not cut reflective metals?
CO2 laser cutters cannot cut reflective metals (brass and aluminum). It is because the laser beam reflects off the metal surface, thus reducing its effectiveness.
It can cause the laser to lose energy and not be able to cut the metal. To overcome this, we can use a process called “metal Surface Treatment” before using these cutter machines.