Various industries use CO2 lasers, including medicine, research, and manufacturing. They are known for their high power and precise cutting abilities. We will discuss how does the co2 laser work?
Gas lasers produce a beam of light by combining carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium, and other gases.
We will explore the basics of carbon dioxide lasers in this article. It will include how they work, their applications, and their advantages and limitations.
Basics of CO2 Laser

The Gain Medium of these lasers contains a combination of gases containing up to 20 % of each carbon and nitrogen gas and 60 % helium. Gas mixtures are excited with electrical current to produce laser beams.
The excited gas molecules release photons, which bounce back and forth between two mirrors in a resonator. As the photons bounce back and forth, they become more concentrated and form a coherent light beam.
These lasers produce wavelengths of 10600 nm, which lies in the infrared region in the electromagnetic spectrum. CO2 lasers are best for working on non-metals.
How Does the CO2 Laser Work?
The concept of population inversion or stimulated emission is necessary to understand how a CO2 laser works. It occurs when several excited atoms or molecules in a material exceed the number of ground-state atoms or molecules.
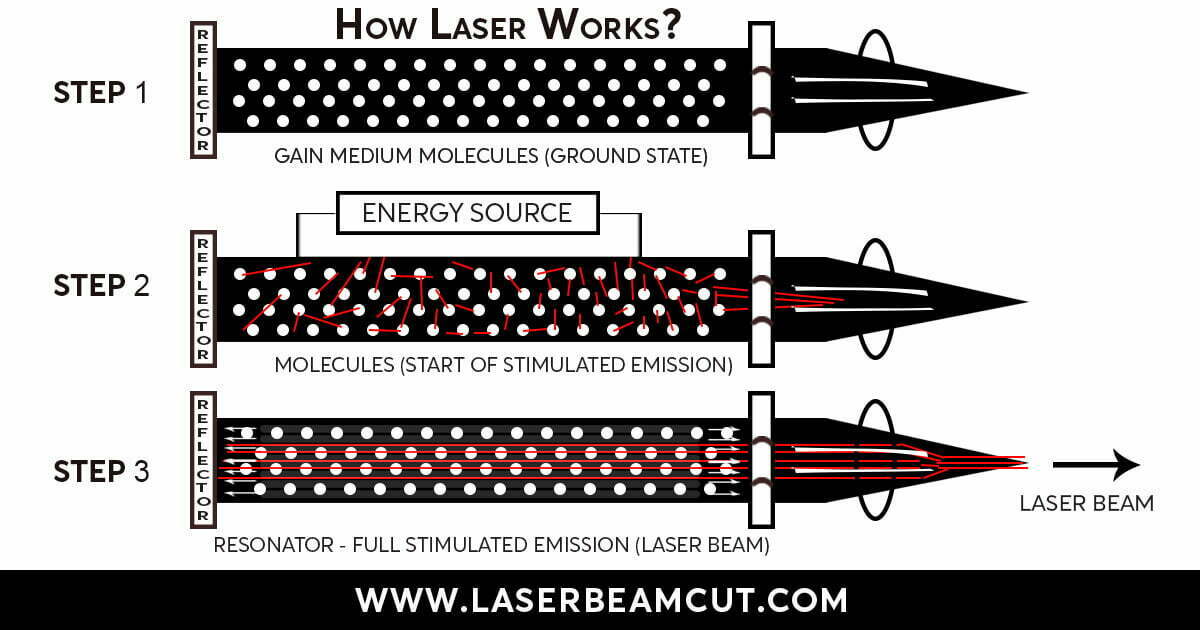
Step 2 of CO2 lasers involves an electrical current that excites the gas mixture. In step 3, the creation of a population inversion starts.
These photons are then reflected back and forth between two mirrors in a resonator or optical cavity. It amplifies the light and produces a high-power laser beam.
Power Ranges of CO2 Lasers
These devices come in the market with different power ranges. The below tables give you a general overview of CO2 laser powers.
| Laser Power | Application |
| 10-20 watts | Marking, engraving, and light cutting of materials like wood, leather, and plastics |
| 20-50 watts | Cutting and engraving of thicker materials such as acrylic and rubber |
| 50-100 watts | Cutting and engraving of thick materials like leather, stainless steel, and glass |
| 100-150 watts | High-speed cutting and engraving of thick materials, as well as some industrial applications |
| 150-500 watts | Heavy-duty cutting and industrial applications, such as cutting and welding of materials |
Applications of Carbon Dioxide Lasers
These lasers have various applications in industries such as medical and manufacturing industries.
Medical applications
Carbon dioxide lasers are popular in the medical industry due to their precision, minimal invasiveness, and versatility.
- Use in Dermatology for skin treatment
- Use in Gynecology for vaginal procedures
- Use in Ophthalmology for eye surgeries
- Use in ENT surgeries
Manufacturing Industry Applications
These lasers can perform various operations in manufacturing industries.
- Use to Weld metals and plastic materials
- Material marking and engraving applications
- Used in 3D printing materials
Advantages and Limitations of CO2 Laser
Advantages
- High precision
- Minimal invasiveness
- Versatility
- Fast processing
- Greater customization
- Reduced scarring
- Improved outcomes
Limitations
- Not suitable for all materials
- Eye damage risk
- Fire hazard
- Limited depth of penetration
- Operator training needed
Conclusion
Hopefully, this article has shed some light on the question, “How does the CO2 laser work?” CO2 lasers have revolutionized various industries with their precision, versatility, and fast processing capabilities.
We have explored the basics of CO2 lasers, including their applications, power ranges, advantages, and limitations. However, operating these powerful tools requires proper training and safety precautions to avoid any risks of injury or damage.
FAQs of CO2 Laser and How Does it Work
1. Does CO2 laser cutting work on all types of materials?
No, CO2 lasers are best for cutting non-metals such as wood, plastics, fabrics, and leather, as well as some metals such as stainless steel.
2. What makes CO2 lasers popular in the medical industry?
CO2 lasers are popular in the medical industry due to their precision, minimal invasiveness, and versatility in treating various skin, gynecological, ophthalmological, and ENT conditions.
3. Can CO2 lasers be used for 3D printing?
CO2 lasers enable the 3D printing of metal parts by melting and fusing metal.
4. What is the maximum depth of penetration of CO2 lasers?
The maximum penetration depth of CO2 lasers is limited to a few millimeters, which is why they are better suited for surface treatments such as cutting, marking, and engraving.
5. What are the safety considerations when using CO2 lasers?
CO2 lasers pose a risk of eye damage, fire hazards, and skin burns, so operators should wear protective gear, ensure proper ventilation, and receive adequate training before using these lasers.

