In the world of manufacturing, technology has transformed the industry significantly. A significant technological advancement in the manufacturing industry is the industrial laser.
An industrial laser is a tool that uses a high-powered beam of light to cut, shape, and engrave materials. The laser industry has revolutionized manufacturing processes, making them faster, more precise, and more efficient.
This article will discuss industrial laser devices in detail with their comparison with science laser types.
What Is Industrial Laser System?
An industrial laser system is a complex machine that generates and delivers high-powered laser beams to perform a variety of industrial applications. Usually, these systems comprise a laser source, optics, and control software. The primary objective of designing these machines is to carry out various tasks, including cutting, welding, marking, engraving, drilling, and many others.

It is possible to customize industrial laser systems to meet specific production requirements. Automotive, aerospace, electronics, and healthcare industries use them.
In contrast, researchers and scientists design scientific lasers for conducting exacting experiments and research applications. These science laser types use in scientific labs and domestic applications, like playing with cats and dogs, catching public attention, and performing various other tasks.
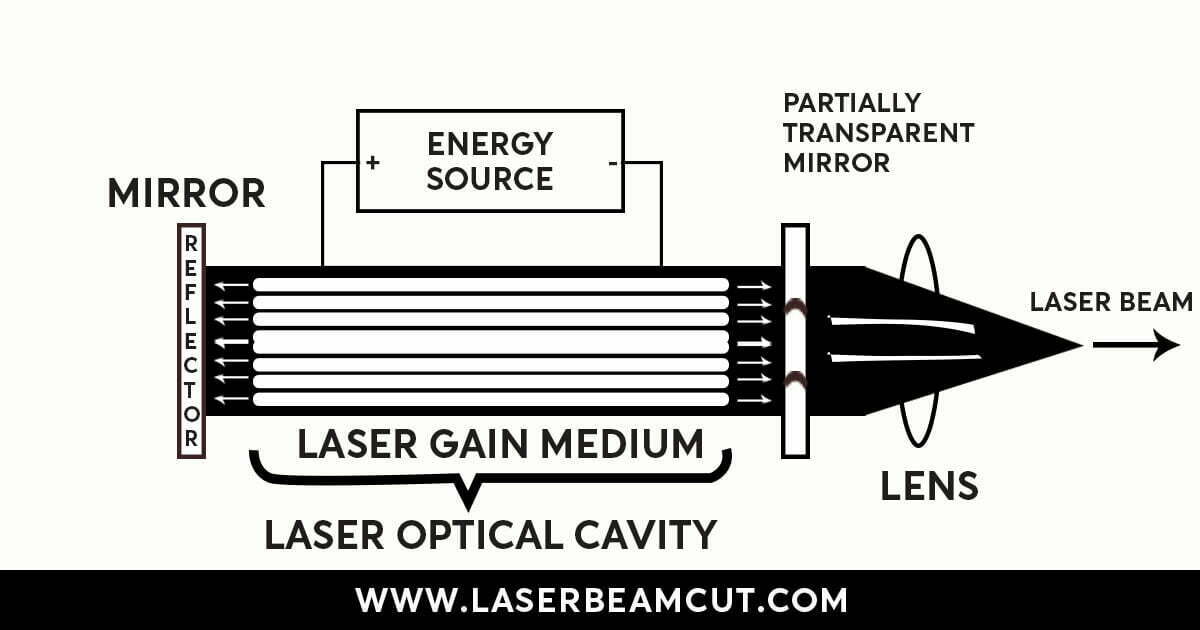
Design of Laser Industrial Devices
Laser design depends on the three main components of the laser.
- Gain Medium – Fiber, CO2 laser types depend on the Gain medium material.
- Power Source – It may be a pump, electric, or gas.
- Mirrors
Classification of Lasers
- They come in different types based on the medium of the laser, including
- CO2 lasers
- Fiber lasers
- Nd: YAG lasers
- Diode lasers
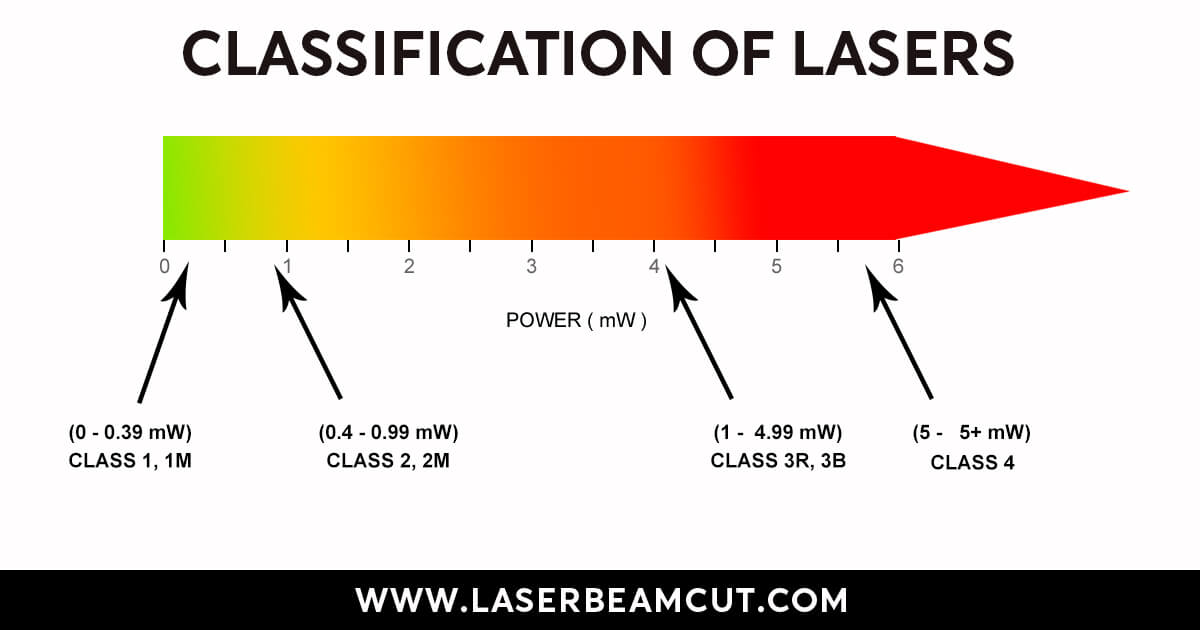
- Experts classify these lasers into four safety classes based on safety norms.
- Class 1
- Class 2
- Class 3
- Class 4
- They come in different types based on the medium of the laser, including
Read Our blog about lasers for more details: https://laserbeamcut.com/classification-of-lasers/
Comparison of Industrial Laser VS Scientific Laser
The main differences between scientific and industrial lasers are:
| Scientific Lasers | Industrial Lasers | |
| Purpose | Research and scientific applications | Manufacturing and industrial applications |
| Beam Quality | High beam quality and stability for precise experiments | High power and efficient beam for industrial applications |
| Complexity | Can be highly complex and specialized for specific experiments | Designed for ease of use and reliability in production environments |
| Control | Precise control over beam parameters for scientific experimentation | Control over power and speed for manufacturing processes |
Environment | Typically used in controlled laboratory environments | Used in various conditions, from factories to construction sites |
Cost | Higher cost due to specialized equipment and precision | Less expensive due to efficient design and high-volume production |
Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance and calibration | Designed for low maintenance and high durability |
Applications | Spectroscopy, microscopy, particle acceleration, etc. | Cutting, welding, marking, engraving, drilling, etc. |
Advantages of Industrial Lasers
The use of the laser industry in manufacturing comes with many benefits. Here are some of the advantages:
- Precise manufacturing with lasers
- Faster production, lower costs
- Lasers work with many materials
- Less waste with precision
- Safer than traditional tools
Industrial Laser Applications
The use of industrial lasers is not limited to one industry. They have found applications in many sectors, including.
Industrial laser Cleaner
It uses high-intensity laser beams to remove rust, paint, oil, and other contaminants from metal surfaces. Its energy vaporizes the material impurities, leaving a clean surface without damaging the substrate.

This process is faster and more environmentally friendly than traditional cleaning methods such as sandblasting or chemical cleaning. Laser cleaning is also more precise, allowing for selective cleaning of specific areas.
Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing utilize industrial laser cleaners. These cleaners are particularly advantageous for cleaning intricate parts and areas that are difficult to access.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies heavily on industrial lasers for a range of applications. Industrial laser cutter machines precisely cut parts in aircraft engines and structures, while industrial marker machines use to mark their components.

The laser ignition system uses a laser beam to ignite the fuel-air mixture, resulting in a more efficient and reliable combustion process. Laser ignition systems are more reliable than traditional spark ignition systems and can also reduce emissions, making them an environmentally friendly option.
Medical Industry
Medical professionals widely use lasers for various procedures. For instance, laser surgery is a common approach for eye surgery, cosmetic procedures, and cancer treatment.
Lasers offer high precision and minimize tissue damage, leading to faster healing and reduced patient pain.

Dentists employ diode lasers for various procedures, including teeth whitening, cavity removal, and gum surgery.
Scientists and engineers utilize lasers in tissue engineering to produce precise patterns on biocompatible materials, which facilitate new tissue growth.
Material Processing
Manufacturers commonly use industrial lasers for cutting, drilling, welding, and surface treatment of various materials. The high precision and accuracy of lasers enable the production of complex shapes and designs with minimal waste.
- The use of laser cutting is particularly beneficial in creating sharp corners and intricate patterns on a wide range of materials: metals, plastics, and others.
- It uses laser welding to join thin materials or dissimilar metals.
- Laser drilling can create precise holes in a variety of materials.
- Laser surface treatment modifies the surface properties of materials, such as hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Electronics Industry

The electronics industry utilizes industrial lasers for cutting, drilling, and marking circuit boards and semiconductor materials. It ensures the precise and efficient production of PCB circuit boards.
Future of Industrial Lasers
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT) has a close connection with the future of industrial lasers. Integration of AI and IoT in industrial laser systems can enhance process control, automation, and data analysis.
For example, AI algorithms can optimize laser parameters to achieve higher efficiency and quality, while IoT sensors can collect data on laser performance and provide real-time monitoring and control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, industrial lasers have revolutionized the manufacturing industry by making the process faster, more precise, and more efficient. Industrial lasers come in different types based on the medium of the laser. These devices use for high-volume manufacturing and industrial applications.
They have many advantages, including precise manufacturing, faster production, less waste, and increased safety. Laser industrial devices have applications in various industries, including aerospace, medical, material processing, and electronics.
AI and IoT integration in industrial laser systems improve automation, data analysis, and process control, leading to more efficient and precise manufacturing processes and a higher demand for industrial lasers.
FAQs About Industrial Laser Devices
1. Can laser cleaning cause damage to metal?
Ans: Yes, laser cleaning can cause damage to the metal if the laser intensity or duration is too high.
2. What is the most significant risk of using lasers?
Ans: The most significant risk of using lasers is eye damage. It causes due to not taking adequate safety measures during the operation of these devices.
3. How do industrial lasers impact mechanical operations?
Ans: Industrial lasers improve mechanical operations by offering high precision, speed, and flexibility in material processing, welding, cutting, and drilling applications.
4. What is the main difference between scientific and industrial lasers?
Ans: Scientific lasers are for research, and industrial lasers are for manufacturing.
5. What is the future of industrial laser devices?
Ans: The future of industrial lasers is promising, with advancements in artificial intelligence and the internet of things allowing for improved automation, data analysis, and process control, transforming the manufacturing industry.

